
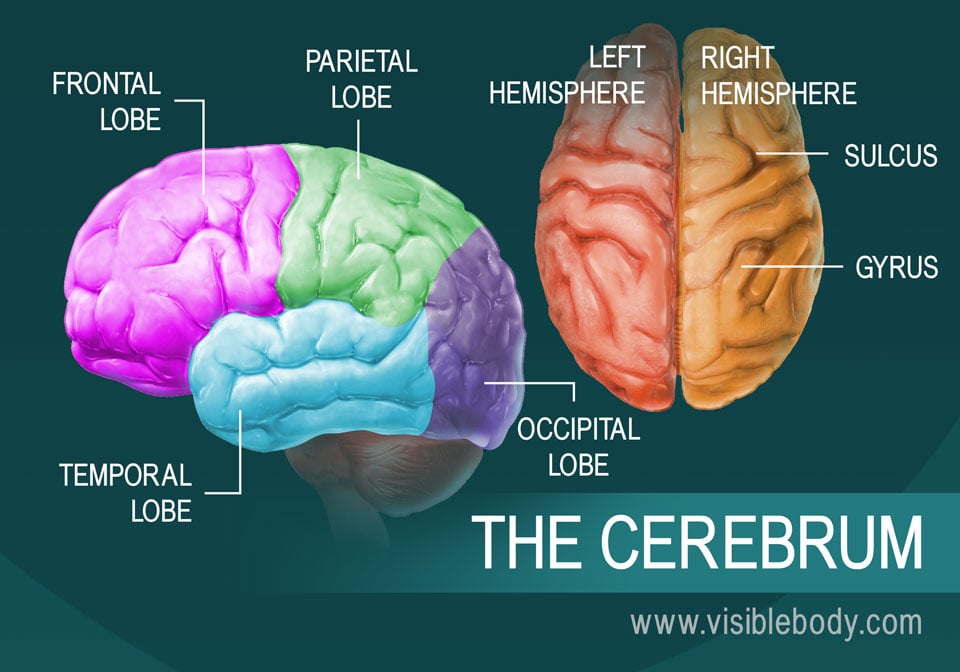
And diencephalon, in turn, sends information to the primary visual cortex, called the sensory cortex.įrom the primary sensory cortex, nerve signals are sent to the adjacent areas and are called sensory associative cortex areas. The nerves then transmit information to the diencephalon, another part of the brain. Light signals transmit information to the occipital lobe via nerve endings, which represents a form of irritation or stimuli for the retina. This is the process that happens if there is a damage on the surface of the primary visual cortex. Generally, everything projected by the retina is recognized and formed into a specific image in the occipital lobe.įor absolutely healthy people, this proportion works independently and flawlessly, but irreparable consequences can occur with injuries and some illnesses. Accordingly, we remember the name of the place of destination and remember it as we move along this route.Īs we have already stated, the occipital lobe is responsible for the visual perception of information, as well as its operational storage. to process different signals perceived by the photosensitive cells of our retina.įurthermore, the occipital lobe receives incoming information, which is processed and immediately sent to the hippocampus, where it is formed into memory.

When we look at a map and "put" the route planner information into our working memory, the first step would be to process millions of light stimuli in the recognition centers, i.e. Different types of sensitivities are synthesized in this visual area, more complex visual images emerge and they are recognized.Īn example can be given to understand the function of the occipital lobe in visual perception. The neurons of these zones are polymodal and respond not only to light but also to tactile and auditory stimuli.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
